A new module in the known TrickBot attack is now is discovered. The new development allows attackers to leverage compromised systems and launch a brute force attack against Windows systems running an RDP connection exposed to the Internet.
TrickBot is a banking Trojan that usually acts as a dropper for other malware. It uses a man-in-the-browser attack to steal financial information. A man-in-the-browser attack is a proxy Trojan that infects a web browser, by leveraging the browser's vulnerabilities. It modifies web pages, transaction content or inserts additional transactions, all invisible to the user and the host. Some of TrickBot's modules abuse the SMB protocol to spread the carried malware laterally across the network. If this is the case, the malware can easily spread in the organization, since hardware and software configurations in a system tend to be homogeneous.
TrickBot's attack method until now:
Systems usually get infected by TrickBot via spam mail campaigns. The malspam campaigns that deliver TrickBot use third party branding familiar to the target, such as Microsoft documents. The opened attachment allows executing a VBScript to run a PowerShell script and download the malware. TrickBot can check it doesn't run in a sandbox environment and to disable antivirus programs, such as Microsoft's Windows Defender. Once executed, TrickBot redeploys itself in the "%AppData%" folder and create a scheduled task to provide persistence.
TrickBot determines the infected host's public IP address and starts receiving instructions from the command-and-control (C2) server. The TrickBot is then ready to download modules that are sent with a configuration file. The C2 servers constantly change and the TrickBot infection is updated with the new information, continuing to download modules. Those modules perform tasks for stealing banking information, system/network reconnaissance, credential harvesting, and network propagation.
Emotet, TrickBot & Ryuk Attack Can Be Mitigated With Hardening
The New TrickBot RDP Brute Force Method:
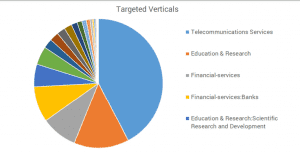
The current campaign is targeting mainly telecommunication services, education, and financial services companies.
The phishing campaign uses an email distinguished as a tax incentive notification from a financial services company. The email contains a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that claims to contain details of tax incentives. However, this attachment is obviously malicious and will download and deploy TrickBot on the user's machine.
How it works:
At the beginning of its execution, TrickBot creates a folder containing encrypted malicious payloads and their configuration files. The configuration files include a list of C2 servers that the plugin needs to communicate with to retrieve the commands that need to be executed.
The rdpScanDll plugin shares its configuration file with a "vncDll" module and uses a standard URL format to communicate the new C2 servers. The URL is: https://C&C/tag/computerID/controlEndpoint
Different sections in this URL refers to different objects:
* C&C= refers to the C2 server
*tag- refers to the group tag used by TrickBot.
*computerID= refers to the computer ID that is used by the malware.
*controlEndPoint= refers to a list of attack methods and a list of IP address number combinations to be targeted via the RDP brute-force attack.
The C2 tells the plugin what kind of attack module should be used. This version of TrickBot has three attack modules:
*Check' mode- checks for an RDP connection from the targets list.
*’Trybrute' mode- attempts a brute force attack on a selected target. It uses a predetermined list of usernames and passwords he got from the endpoints "/RDP/names" and "/RDP/dict".
*Brute mode- still in the development phase.
The C2 also commands the module on which port to target (RDP port is the default), how ferequently to report status back to the server, which port pairs to move on to when the current list is exhausted, and which username and password to try and brute force.
Once the first IP list (gathered via "/rdp/domains") is exhausted, the plugin sets another IP list using a second "/rdp/over" endpoint.
CalCom's hardening recommendations against TrickBot:
- Disable unnecessary RDP/terminal services.
2. Restrict RDP/terminal services on all levels. Enforce best practice secure configuration:
*limit connections.
*limit devises redirection.
*use network-level authentication and limit authentication types.
*limit RDP groups and RDP user's rights assignment authorizations.
3. configure Tunneling Remote Desktop connections through IPSec or SSH.