What is Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
The OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) protocol belongs to a category of IP Routing protocols and serves as an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) designed for the Internet. It is employed to disseminate IP routing details across a solitary Autonomous System (AS) within an IP network.
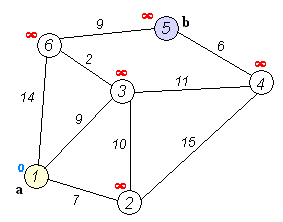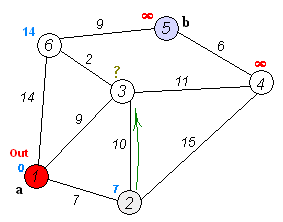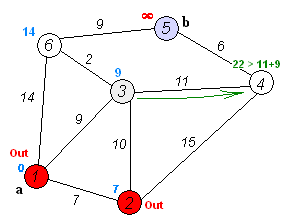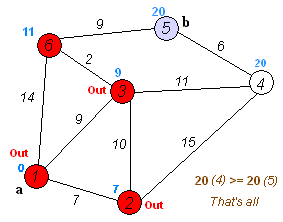
The OSPF protocol operates as a link-state routing protocol, signifying that routers share topology information with their immediate neighbors. This information is disseminated across the Autonomous System (AS), ensuring that each router within the AS possesses a comprehensive understanding of the AS’s topology. Using a variant of the Dijkstra algorithm, routers utilize this knowledge to compute end-to-end paths through the AS. Consequently, in a link-state routing protocol, the selection of the next hop address for forwarding data is based on choosing the optimal end-to-end path leading to the final destination.
(Reference: Wikipedia Contributors, Dijkstra algorithm [Digital Image])
BGP and OSPF are which type of protocol?
BGP facilitates inter-domain routing between diverse organizations, while OSPF handles intra-domain routing within a single organization or network.
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) are both examples of routing protocols. Both protocols are essential for ensuring efficient and reliable communication in the broader internet and private networks.
BGP and OSPF key differences
Understanding the key differences of BGP vs OSPF is crucial for designing and managing networks effectively.
| FEATURE | OSPF | BGP |
| Scope | Within a single AS | Between different ASes |
| Protocol Type | Link-state routing protocol | Path vector routing protocol |
| Convergence | Fast | Slower, but handles complex internet routing |
| Metrics | cost, bandwidth, and delay | Paths, policies, attributes |
| Relationships | Neighbor relationships between routers | Peering relationships between ASes |
How to configure OSPF routing protocol?
To configure the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol here is a general outline of the steps involved:
- Enable OSPF on Router Interfaces:
- Access the router configuration mode.
- Enter the router ospf process-id command, where process-id is a unique number for the OSPF process.
- Use the network network-address wildcard-mask area area-id command to specify which interfaces participate in OSPF and their associated area.
- Set OSPF Area:
- Divide your network into logical areas for better scalability and traffic control.
- Assign interfaces to appropriate areas using the area area-id parameter in the network command.
- Configure OSPF Router ID:
- Each router needs a unique ID within the OSPF domain for identification and to elect a Designated Router (DR) in multi-access networks.
- Set the Router ID using router-id ip-address command or let it be automatically chosen based on the highest IP address on a loopback interface.
- Adjust OSPF Timers (Optional):
- Modify default timers for OSPF neighbor relationships and route updates if needed.
- Use commands like timers basic hello-interval dead-interval and timers lsa arrival ignore-time hold-time.
- Configure Authentication (Optional):
- Secure OSPF routing updates with authentication if required.
- Use ip ospf authentication message-digest for MD5 authentication or ip ospf authentication-key key for simple password authentication.
- Customize OSPF Behavior (Optional):
- Fine-tune OSPF behavior with additional commands for specific scenarios:
- Set default routes: default-information originate
- Adjust route summarization: area area-id range ip-address mask
- Configure virtual links: area area-id virtual-link router-id
- Verify OSPF Configuration:
- Use commands like show ip ospf neighbor, show ip ospf interface, and show ip route ospf to verify OSPF operation and routing table entries.
Remember: Specific commands and syntax vary depending on the router vendor and operating system.
Hardening the configuration of OSPF
The process of hardening the configuration of OSPF involves implementing security measures and best practices to protect the OSPF routing protocol and the network it operates in.
Managing hardened OSPF securely does not scale as the network grows if done manually router-by-router. Without automation, subtle inconsistencies or human errors are likely to creep into OSPF hardening across different routers.
Automation is key for large or complex environments. Tracking down what is specifically configured on routers as it relates to security controls allows the operating systems to always be audit ready and compliant.
Automating the hardening of OSPF configurations not only saves precious time but also amplifies visibility within scalable systems, fostering an agile and highly responsive network environment.