In this article we will provide information regarding the RDS: Do Not Allow Drive Redirection setting.
This blog post will cover:
- What is RDS Drive Redirection policy
- The potential vulnerability in this setting
- Countermeasures for mitigating this vulnerability
- The potential impact of the configuration change
- The setting’s default value
- CalCom’s recommended value
- How to change the configuration
POLICY DESCRIPTION:
This policy specifies whether to prevent the mapping of client drives in a Remote Desktop Services session.
By default, an RD Session Host server maps client drives automatically upon connection. Mapped drives appear in the session folder tree in Windows Explorer or Computer in the format <driveletter> on <computername> . This setting overrides this behavior.

POTENTIAL VULNERABILITY:
A user that’s connecting to a terminal server can choose which drives to redirect to the remote server, including mapped network drives.
There is danger in users that redirect local and mapped drives regardless of whether they need it. Those mapped drives may contain sensitive data.
If the status is set to Disabled, client drive redirection is always allowed. If the status is set to Not Configured, client drive redirection is not specified at the Group Policy level. However, an administrator can still disable the client drive redirection by using the Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration tool.
COUNTERMEASURES:
Preventing users from sharing the local drives on their client computers with Remote Session Hosts that they access helps reduce possible exposure of sensitive data.
If the status is set to Enabled, client drive redirection is not allowed in Remote Desktop Services sessions.
POTENTIAL IMPACT:
Drive and information in it can't be accessed by the RDP client.
CALCOM'S RECOMMENDED VALUE:
Enable

HOW TO CONFIGURE:
Windows 2016 server:
In Windows 2016, these settings are controlled within Group Policy.
- Launch "msc".
- Navigate to "Computer Configuration" > "Administrative Templates" > "Windows Components" > "Remote Desktop Services" > "Remote Desktop Session Host".
- Ensure "Do not allow Drive redirection" is set to "Enabled".
Windows 2012 server:
- Open "Server Manager".
- Select "Remote Desktop" Services.
- Select "Collections".
- Select "Tasks", then choose "Edit Properties".
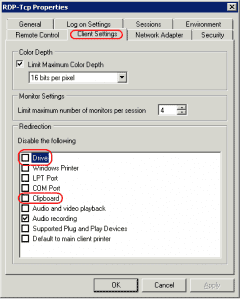
- Under the "Client Settings" tab, ensure the "Drive" is disabled.
Windows 2008 server:
- Launch "Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration" from the server.
- Under "Connections", right-click the connection and select "Properties".
- Select the "Client Settings" tab, and make sure the "Drive" box is checked. Click OKwhen done.
Server hardening can be a painful procedure. If you’re reading this article, you probably already know it. Endless hours, labor, and money are invested in this process, which can often result in production breakdown despite the effort to prevent it. CSH by CalCom is automating the entire server hardening process. CHS’s unique ability to ‘learn’ your network abolishes the need to perform lab testing while ensuring zero outages to your production environment. CHS will allow you to implement your policy directly on your production hassle-free. want to know more? Click here and get the datasheet.